Guides
Firearm Performance
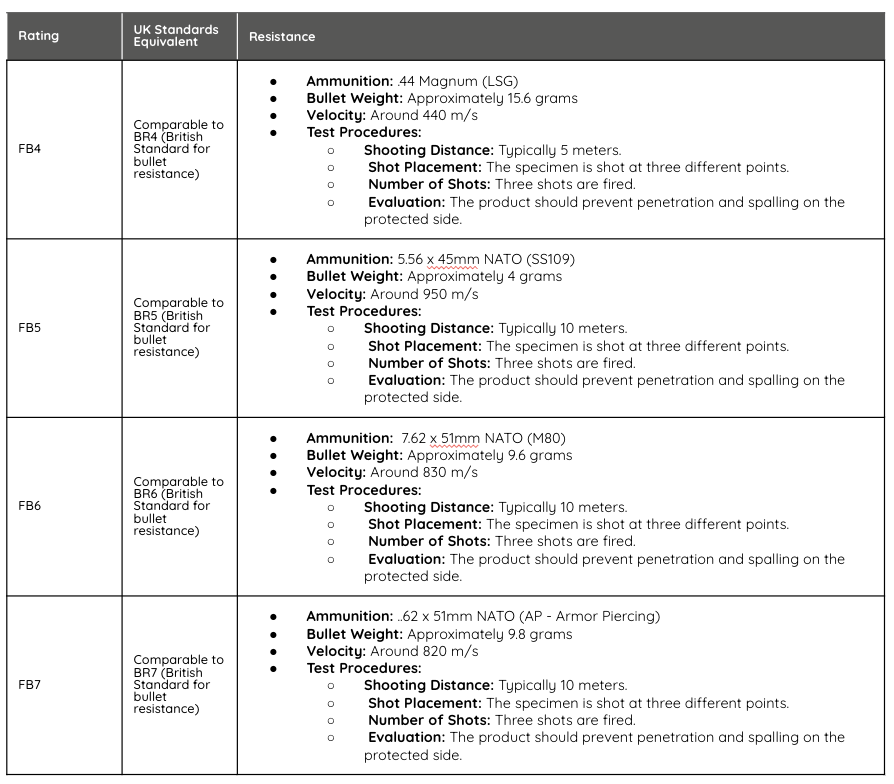
FB4 (.44 Magnum): The .44 Magnum is a handgun round, and it's designed for impact with a large, heavy bullet. The weight is approximately 15.6 grams (240 grains), making it heavier but slower compared to rifle rounds. It is designed to deliver a significant amount of energy on impact, which is why it is used to test against powerful handgun threats.
FB5 (5.56 x 45mm NATO), FB6 (7.62 x 51mm NATO), and FB7 (7.62 x 51mm NATO AP): These rounds are rifle calibers. Rifle bullets are typically lighter but are fired at much higher velocities, which gives them greater kinetic energy and penetration power, especially over longer distances. For example:
- FB5 (5.56 x 45mm NATO): Bullet weight is around 4 grams, but it's fired at around 950 m/s.
- FB6 (7.62 x 51mm NATO): Bullet weight is around 9.6 grams, with a velocity of about 830 m/s.
- FB7 (7.62 x 51mm NATO AP): Bullet weight is about 9.8 grams, designed to penetrate armor.
The classification of bulletproof or ballistic-resistant windows, doors, and other building components is governed by various standards. In Europe, the EN 1522 and EN 1523 standards provide guidelines for testing and classifying bullet resistance. These standards define resistance levels such as FB3, FB5, and FB6, which indicate the product's ability to withstand different calibres of bullets and the energy they deliver. Here’s how these classifications are measured:
1. Standards Overview
- EN 1522: Defines the requirements and classification for bullet-resistant construction.
- EN 1523: Describes the test methods to determine the bullet resistance.